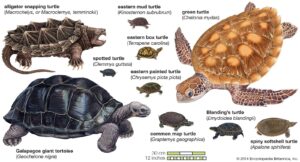
Yes, a turtle is a reptile. Turtles belong to the reptile class, just like snakes, lizards, and crocodiles.
Turtles have been fascinating creatures for millions of years. They are known for their unique shells and slow movements. But many people wonder about their classification. Are turtles reptiles? The answer is yes. Turtles share many characteristics with other reptiles, such as laying eggs and having scaly skin.
They are cold-blooded animals and need the sun to regulate their body temperature. Understanding these traits helps us appreciate turtles even more. In this blog post, we will explore why turtles are classified as reptiles and what makes them unique among other reptiles. Let’s dive into the world of turtles and discover more about these amazing creatures.
Introduction To Turtles
Turtles are fascinating creatures that have captured human interest for centuries. Their unique shells and slow movements make them easily recognizable. But what exactly are turtles? Are they reptiles? Let’s dive into the world of turtles and learn more about these amazing animals.
Brief History
Turtles have been around for millions of years. They first appeared during the Triassic period, over 200 million years ago. These ancient creatures have survived many changes in the Earth’s climate. Their tough shells provide protection from predators. This has helped them thrive through the ages.
Global Distribution
Turtles live all around the world. They can be found in oceans, rivers, and lakes. Some turtles even live in deserts. Different species adapt to various environments. Sea turtles prefer warm, tropical waters. Freshwater turtles live in rivers and ponds. Some turtles migrate long distances. Others stay close to their birthplace.

Credit: www.britannica.com
Defining Reptiles
Reptiles are a class of animals. They are cold-blooded and have backbones. These creatures lay eggs or give birth to live young. Most reptiles have scales on their bodies. They inhabit various environments around the world.
Characteristics Of Reptiles
Reptiles share common traits. Understanding these traits helps identify them easily.
- Cold-blooded: Reptiles rely on external heat sources.
- Scales: Their bodies are covered with scales.
- Egg-laying: Most reptiles lay eggs, but some give birth to live young.
- Lungs: All reptiles breathe using lungs, unlike amphibians.
- Vertebrates: Reptiles have a backbone.
Common Reptile Species
There are many types of reptiles. Each has unique features and habitats.
| Reptile | Description | Habitat |
|---|---|---|
| Turtles | Shell-covered reptiles. Found in water and on land. | Oceans, rivers, and forests. |
| Snakes | Legless reptiles. Some are venomous. | Forests, deserts, and grasslands. |
| Lizards | Reptiles with four legs. Some can change color. | Deserts, forests, and homes. |
| Crocodiles | Large, water-dwelling reptiles. Have powerful jaws. | Rivers and wetlands. |
Reptiles are fascinating creatures. Their unique traits set them apart. Turtles, for example, are easily identified by their shells. Knowing these characteristics helps us understand and appreciate reptiles better.
Turtle Anatomy
The anatomy of a turtle is a fascinating topic. Turtles are reptiles with unique features. Their anatomy helps them survive in various environments. This section delves into their shell structure and internal organs.
Shell Structure
The shell is a crucial part of a turtle’s anatomy. It consists of two main parts:
- Carapace: The top part of the shell. It protects the turtle.
- Plastron: The bottom part of the shell. It covers the belly.
The carapace and plastron are connected by a bridge. The shell is made of bone and cartilage. It is covered by scutes, which are plates made of keratin. These scutes help protect the turtle from predators.
The shape and size of the shell can vary. It depends on the species of the turtle. Some have domed shells, while others have flat ones. The shell also plays a role in the turtle’s buoyancy in water.
Internal Organs
Turtles have internal organs similar to other reptiles. These organs are adapted to their lifestyle. Here are some key internal organs:
- Heart: A turtle’s heart has three chambers. It pumps blood throughout the body.
- Lungs: Turtles breathe air using their lungs. Even aquatic turtles need to surface for air.
- Liver: The liver helps in digestion and detoxification.
- Stomach: The stomach breaks down food for digestion.
- Intestines: Nutrients are absorbed in the intestines.
- Kidneys: Kidneys filter waste from the blood.
Turtles also have a cloaca. It is a multipurpose opening. It is used for excretion and reproduction. Their internal organs are well-protected by the shell. This provides them with a strong defense mechanism.

Credit: www.activewild.com
Behavioral Traits
Turtles are fascinating creatures with unique behavioral traits. Understanding these traits helps us appreciate them better. Let’s explore their habitat preferences, diet, and feeding habits.
Habitat Preferences
Turtles live in various environments. Some turtles prefer aquatic habitats like ponds, lakes, and rivers. These turtles are excellent swimmers. They have webbed feet and streamlined bodies.
Other turtles thrive in terrestrial habitats. These include forests, deserts, and grasslands. Terrestrial turtles, also known as tortoises, have sturdy legs and domed shells.
There are also semi-aquatic turtles. These turtles spend time both in water and on land. They often bask on rocks or logs to warm up.
Diet And Feeding
Turtles have diverse diets. Many turtles are omnivores. They eat both plants and animals. Aquatic turtles often eat fish, insects, and aquatic plants.
Terrestrial turtles, like tortoises, primarily eat plants. Their diet includes grasses, fruits, and vegetables.
Some turtles are strictly carnivorous. These turtles hunt for prey like fish and small invertebrates.
The table below summarizes the diet preferences of different types of turtles:
| Type of Turtle | Diet |
|---|---|
| Aquatic Turtles | Fish, insects, aquatic plants |
| Terrestrial Turtles (Tortoises) | Grasses, fruits, vegetables |
| Carnivorous Turtles | Fish, small invertebrates |
Observing a turtle’s feeding behavior is intriguing. They are patient hunters and careful foragers. They use their strong jaws to chew their food thoroughly.
Understanding their diet is essential for their care in captivity. Providing a balanced diet ensures their health and longevity.
Reptilian Features In Turtles
Turtles are fascinating creatures. They have many traits that classify them as reptiles. This section explores these features in detail.
Cold-blooded Nature
Turtles are cold-blooded animals. This means they cannot regulate their body temperature internally. Instead, they rely on their environment to stay warm or cool.
For instance, on a sunny day, you might see a turtle basking in the sun. This behavior helps them absorb heat. At night, they find a cool spot to rest. This reliance on the environment is a key reptilian trait.
Reproduction And Life Cycle
Turtles have a unique reproductive system. Female turtles lay eggs. These eggs are typically buried in sand or soil to protect them.
Here is a simple table showing the turtle’s life cycle stages:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Egg | Laid in nests, often in sand or soil. |
| Hatchling | Young turtles break out of their eggs. |
| Juvenile | Small turtles that begin to grow and explore. |
| Adult | Fully grown and capable of reproduction. |
Turtles also have a long lifespan. Some can live for over 100 years. This long life is another characteristic of reptiles. The slow growth and delayed maturity are typical in many reptilian species.

Credit: www.greeleypetvet.com
Scientific Classification
Understanding the scientific classification of turtles helps us know their place in the animal kingdom. It outlines their relationship with other creatures and explains why turtles are classified as reptiles.
Taxonomic Hierarchy
The taxonomic hierarchy is a system used by scientists to organize living organisms. Turtles fall under the following categories:
| Category | Classification |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Reptilia |
| Order | Testudines |
| Family | Varies by species |
| Genus | Varies by species |
| Species | Varies by species |
Turtles belong to the kingdom Animalia and the phylum Chordata. This means they are animals with a spinal cord. They are part of the class Reptilia, which includes all reptiles.
Comparative Analysis
Comparing turtles with other reptiles shows why they belong in the same class. Here are some key points:
- Cold-blooded: Turtles, like other reptiles, are ectothermic.
- Scales: They have scales, though some are hidden under their shells.
- Egg-laying: Most turtles lay eggs, similar to other reptiles.
Turtles share many traits with other reptiles. They are cold-blooded and lay eggs. Their bodies are covered with scales. This places them firmly within the class Reptilia.
Common Misconceptions
Many people have misconceptions about turtles and their classification. Some think they are amphibians or even mammals. These misunderstandings lead to confusion. Let’s debunk some of these myths and clarify the facts.
Myths Vs. Facts
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| Turtles are amphibians. | Turtles are reptiles. They have scales and lay eggs on land. |
| Turtles can live both in water and on land. | Some turtles live only in water, while others live on land. |
| All turtles have the same type of shell. | Turtle shells vary. Some are hard, some are soft. |
Public Perception
The public often perceives turtles as slow and harmless creatures. This image is not entirely accurate. Some turtles can be quite fast in water. Others can be aggressive if threatened.
- Speed: Aquatic turtles swim quickly.
- Behavior: Snapping turtles can be aggressive.
- Habitat: Turtles adapt to various environments.
Understanding these facts helps correct public perception. Turtles are fascinating reptiles with unique characteristics.
Conservation Efforts
Turtles face many challenges today. Conservation efforts aim to protect these ancient creatures. Efforts focus on reducing threats and preserving their habitats.
Threats To Turtle Populations
Many threats endanger turtles. Pollution damages their habitats. Plastic waste is a major problem. Turtles mistake plastic for food. This can be fatal.
Climate change also affects turtle populations. Rising temperatures alter their nesting sites. It impacts the sex ratio of hatchlings. More females are born, reducing genetic diversity.
Illegal trade poses another threat. Poachers capture turtles for their shells. They sell them as pets or for traditional medicine. This reduces their numbers in the wild.
Protection Strategies
Several strategies help protect turtles. One method is habitat restoration. Cleaning up beaches and oceans removes harmful waste. This creates safer environments for turtles to nest and live.
Creating protected areas is vital. Marine reserves and wildlife sanctuaries offer safe havens. These areas are off-limits to human activities. Turtles can thrive without interference.
Education and awareness campaigns are crucial. Informing the public about turtle conservation helps. People learn the importance of protecting these creatures. They become more mindful of their actions.
Stronger laws and regulations are needed. Governments must enforce bans on illegal trade. Penalties for poachers should be severe. This discourages illegal activities and helps save turtles.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is A Turtle A Reptile?
Yes, turtles are reptiles. They belong to the class Reptilia. This group includes snakes, lizards, and crocodiles.
What Characteristics Define Turtles As Reptiles?
Turtles have scaly skin, lay eggs, and are cold-blooded. These features classify them as reptiles.
Do Turtles Lay Eggs?
Yes, turtles lay eggs. Female turtles dig nests on land to lay their eggs.
Are Turtles Cold-blooded?
Yes, turtles are cold-blooded. Their body temperature depends on their environment.
Conclusion
Turtles are indeed reptiles. They have scales and lay eggs. Their cold-blooded nature classifies them as reptiles. Understanding turtles helps us appreciate their unique traits. They are fascinating creatures, both on land and in water. Learning about turtles can be fun and educational.
So next time you see a turtle, remember it’s a reptile. Share your newfound knowledge with friends and family. Keep exploring the animal kingdom. There’s always something new to discover.