Yes, turtles are reptiles. They belong to the class Reptilia, which includes snakes, lizards, and crocodiles.
These fascinating creatures have been around for millions of years. Turtles are known for their hard shells and slow movements. They live in diverse environments, from oceans to deserts. Understanding their classification helps us appreciate their unique characteristics. Reptiles are cold-blooded, lay eggs, and have scales.
Turtles fit these descriptions perfectly. They regulate their body temperature through their surroundings and have scales covering their bodies. This blog post will explore the features that make turtles reptiles and why they are so important to our ecosystems. Let’s dive in and learn more about these incredible animals.

Credit: www.johnscreekvet.com
Introduction To Turtles
Turtles are fascinating creatures that have roamed the earth for millions of years. They belong to the reptile family, which includes snakes, lizards, and crocodiles. Turtles are known for their hard shells and slow movements. These unique features make them stand out in the animal kingdom. Understanding turtles helps us appreciate their role in nature.
Brief History
Turtles have a rich history that dates back over 200 million years. They first appeared during the time of the dinosaurs. These ancient reptiles have survived many changes in the earth’s climate and environment. Their hard shells provided protection from predators. This made them resilient survivors. Fossils show that turtles have changed little over the ages. This stability shows how well-adapted they are to their environments.
Global Distribution
Turtles can be found on almost every continent. They live in a variety of habitats, from oceans to deserts. Sea turtles swim in the warm waters of the tropics. Freshwater turtles thrive in rivers and lakes. Some species even live in forests and grasslands. The wide distribution of turtles shows their adaptability. They play important roles in their ecosystems. Turtles help control insect populations and disperse seeds. Their presence is vital for maintaining healthy environments.
Classification Of Turtles
Turtles belong to the reptile group. They have hard shells that protect them from predators. Turtles lay eggs on land.
Turtles are fascinating creatures that many people love. But are turtles reptiles? Understanding their classification helps answer this question. Turtles belong to a specific group within the animal kingdom. This section will delve into their scientific classification and the different types of turtles.Scientific Classification
Turtles belong to the class Reptilia. This class includes all reptiles. Within Reptilia, turtles fall under the order Testudines. This order is unique due to the presence of a bony or cartilaginous shell. The shell acts as a shield. It protects the turtle from predators and harsh environments. Turtles have been around for millions of years. Their ancient lineage makes them one of the oldest reptile groups.Types Of Turtles
There are several types of turtles. Each type has unique characteristics. Sea turtles, for example, live in oceans. They have flippers instead of feet. These flippers help them swim long distances. Freshwater turtles, like the painted turtle, live in rivers and lakes. They have webbed feet for swimming. Then there are terrestrial turtles. These are often called tortoises. They live on land and have sturdy legs. Understanding these types helps in knowing more about their habitats. Each type of turtle plays a role in its ecosystem. They are important for maintaining ecological balance. “`Reptilian Characteristics
Turtles are fascinating creatures, often seen basking in the sun or swimming gracefully in water. Many people wonder if turtles are reptiles. To answer this, it’s important to understand the characteristics that define reptiles. By examining these traits, we can see how turtles fit into this classification.
Defining Traits
Reptiles are cold-blooded vertebrates. They rely on external heat sources to regulate their body temperature. This is a key characteristic. They also have dry, scaly skin. This skin helps prevent water loss. Reptiles lay eggs with leathery shells. This protects the eggs from drying out.
Another trait is their breathing system. Reptiles have lungs and breathe air. They also have a three-chambered heart, with the exception of crocodiles, which have a four-chambered heart. These traits are common in all reptiles, including turtles.
Comparison With Other Reptiles
Turtles share many traits with other reptiles like snakes, lizards, and crocodiles. For example, they have scales and lay eggs. But turtles have unique features too. They have a hard shell. This shell is made of bone and is covered in scutes. Scutes are scales made of keratin.
Unlike snakes, turtles cannot unhinge their jaws to eat large prey. They have beaks instead of teeth. This makes their eating habits different. Turtles also have a more developed sense of smell. This helps them find food underwater.
While lizards can regrow lost tails, turtles cannot regrow their shells. Their shells grow with them throughout their lives. Crocodiles are more aggressive and have stronger jaws. They live in both saltwater and freshwater. Turtles, on the other hand, are generally more peaceful and can be found in various habitats.
By understanding these characteristics, we can see that turtles are indeed reptiles. They share many traits with other reptiles but also have unique features that set them apart.
Turtle Anatomy
Turtles are fascinating creatures with unique anatomical features. Their anatomy sets them apart from other reptiles. Understanding turtle anatomy helps us appreciate their remarkable adaptations. This section explores two key aspects of turtle anatomy.
Shell Structure
A turtle’s shell is its most distinctive feature. It consists of two parts: the carapace and the plastron. The carapace is the top part of the shell. It protects the turtle from predators. The plastron is the bottom part. It shields the turtle’s belly. Together, they form a protective armor. The shell is made of bone and cartilage. It is covered by scutes, which are hard scales. Scutes give the shell strength and durability. The shell is not just an outer covering. It is part of the turtle’s skeleton. It includes the spine and ribcage. This makes the shell very strong and rigid.
Unique Physiological Features
Turtles have many unique physiological features. They can breathe with their lungs, like other reptiles. Some turtles can also absorb oxygen through their skin. This helps them stay underwater longer. Their hearts are special too. They have three chambers instead of four. This allows turtles to control blood flow better. It helps them survive in low-oxygen environments. Turtles also have strong limbs. Their legs are adapted for swimming or digging. Sea turtles have flippers for swimming. Land turtles have sturdy legs for walking. These adaptations help turtles thrive in their habitats.
Turtle Habitats
Turtles are fascinating creatures with diverse habitats. They can be found in various environments around the world. Some turtles live in the ocean, others in freshwater lakes and rivers, and some on land. Understanding their habitats helps us appreciate their adaptability and survival skills.
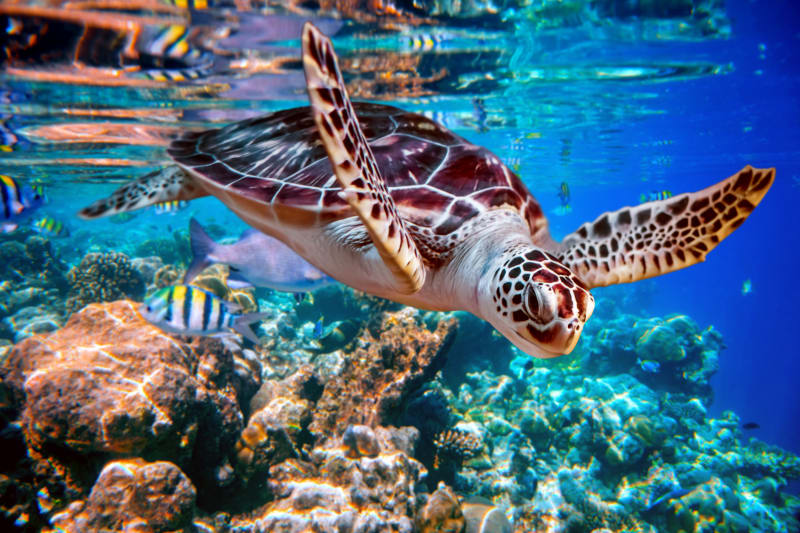
Marine Environments
Many turtles thrive in marine environments. Sea turtles, for example, spend most of their lives in the ocean. They migrate long distances between feeding and nesting sites. Their bodies are streamlined for swimming, and they have flippers instead of feet. Coral reefs, seagrass beds, and open oceans are their primary homes. They feed on jellyfish, seaweed, and small invertebrates.
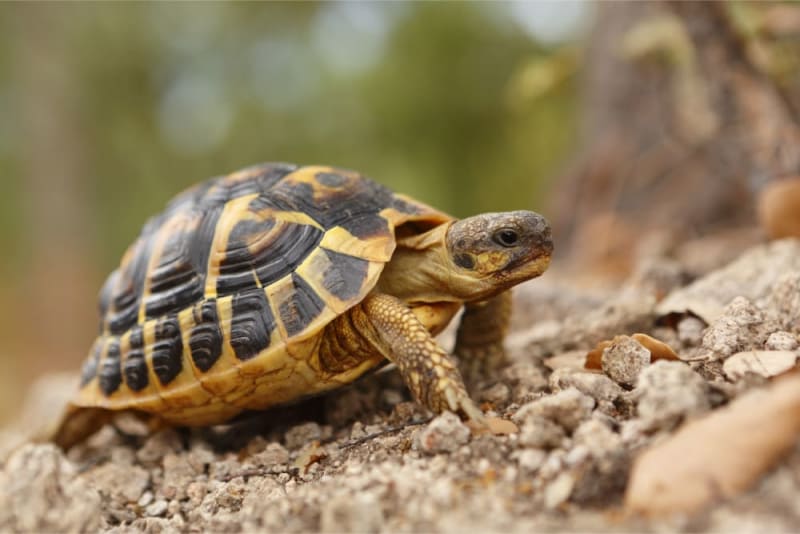
Terrestrial And Freshwater Habitats
Some turtles live in terrestrial and freshwater habitats. These include ponds, rivers, lakes, and forests. Freshwater turtles have webbed feet for swimming but also walk on land. They bask in the sun on logs or rocks. Land turtles, like tortoises, prefer dry environments. They have sturdy legs for walking and digging. They eat plants, fruits, and small insects. Their habitats offer plenty of hiding spots and food sources.

Credit: www.earth.com
Turtle Behavior
Turtles are fascinating creatures with unique behaviors. Understanding their behavior helps us protect them. This section explores their feeding habits, reproduction, and lifecycle.
Feeding Habits
Turtles have diverse feeding habits. Some are herbivores, while others are carnivores or omnivores. Here is a table showing different types of diets:
| Type | Diet |
|---|---|
| Herbivores | Plants, algae, and fruits |
| Carnivores | Fish, insects, and small animals |
| Omnivores | Both plant and animal matter |
Herbivorous turtles munch on leaves and vegetables. Carnivorous turtles hunt for fish and insects. Omnivorous turtles enjoy a mix of both. Turtles use their strong jaws to break down food. They do not have teeth, but their beaks are sharp.
Reproduction And Lifecycle
Turtle reproduction is intriguing. Female turtles lay eggs on land. They dig nests in the sand or soil. The number of eggs varies by species. A clutch can have 50 to 200 eggs.
The eggs incubate for several weeks. Temperature affects the sex of the hatchlings. Warmer temperatures produce more females. Cooler temperatures produce more males. Hatchlings emerge and make their way to water.
Here is the turtle lifecycle in a nutshell:
- Eggs are laid on land.
- Incubation occurs for several weeks.
- Hatchlings emerge and head to water.
- Juveniles grow and mature over years.
- Adults reproduce and continue the cycle.
Turtles can live for decades. Some species live over 100 years. Protecting their habitats ensures their survival.
Common Myths About Turtles
Many people think they know everything about turtles. But there are many myths about these fascinating creatures. Let’s explore some common myths about turtles.
Longevity Myths
People often believe that all turtles live for centuries. This is not true. While some turtles can live very long, not all do. Different species have different lifespans. Some turtles live for 20 years, others much longer. It depends on their species and environment.
Misconceptions About Turtles
Another myth is that turtles are slow and lazy. This is not always the case. Many turtles are quite active and fast in water. They move quickly when they need to. Turtles are not just slow creatures.
Some people think turtles can leave their shells. This is a big myth. A turtle’s shell is part of its body. They cannot leave their shell. It is like our ribcage; it protects vital organs.
Many also believe turtles can live without water. This is not true. Turtles need water to live. They spend a lot of time in water. Water is important for their survival.
Conservation Efforts
Turtles face numerous challenges in the wild. Conservation efforts are crucial for their survival. Dedicated organizations and communities are working tirelessly to protect these ancient creatures. This section delves into the threats facing turtles and the global initiatives to conserve them.
Threats To Turtle Populations
Turtles face habitat loss due to human activities. Pollution and climate change also impact their environments. Poaching for their shells and meat remains a significant threat. Many turtles get caught in fishing nets, leading to injury or death. Coastal development disrupts nesting sites, affecting reproduction rates.
Global Conservation Initiatives
Various global efforts aim to protect turtle populations. Marine protected areas help safeguard their habitats. Organizations work to reduce bycatch in fishing operations. Some initiatives focus on cleaning polluted habitats. Educational programs raise awareness about turtle conservation. Laws and regulations are enforced to prevent illegal trade.

Credit: www.greeleypetvet.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Turtles Classified As Reptiles?
Yes, turtles are classified as reptiles. They belong to the order Testudines. Reptiles are characterized by their scaly skin, and turtles share this trait.
Do Turtles Lay Eggs?
Yes, turtles lay eggs. They usually lay their eggs on land. Female turtles dig nests in the sand or soil.
How Long Do Turtles Live?
Turtles can live for a very long time. Some species can live over 100 years. Their lifespan varies by species.
What Do Turtles Eat?
Turtles have varied diets. Some are herbivores, eating plants and algae. Others are omnivores, eating plants and small animals.
Conclusion
Turtles are fascinating creatures. They belong to the reptile family. Their unique features include shells and cold-blooded nature. Turtles have lived on Earth for millions of years. Understanding their reptile traits helps in their conservation. Knowing turtles better allows us to appreciate their role in the ecosystem.
So next time you see a turtle, remember its ancient lineage.